A rigid rod rotating about the center of the circle holds an object in a vertical circle of radius .5099 meters.
- The highest point of its path,
- the lowest point, and
- a point whose altitude is identical to that of the center of the circle.
The object has uniform speed, so its only acceleration is centripetal:
The net force at any point is the product of mass and acceleration. The magnitude of the net force is therefore that of the centripetal force
Since only the rod and gravity exert forces on the object, at any point the net force on the object is the sum of the forces exerted by the rod and by gravity.
The magnitude of the gravitational force is the weight m * g = 1.759 kg * 9.8 m/s^2 = 17.2382 Newtons
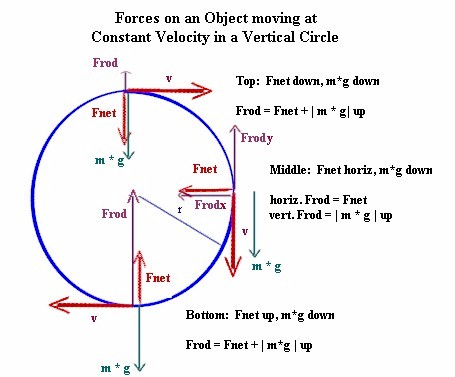
At the top of the arc the net force is toward the center and therefore downward.
- net force = rod force + weight
- rod force = net force - weight = - 3.449 Newtons - (- 17.2382 Newtons) = -3.449 Newtons.
- The object doesn't need a centripetal force as great as that of the weight, so to stay in the circular orbit it must avoid experiencing all the force.
- The rod obliges by supplying an upward force to counter that of the weight.
- [ Actually this is what the rod has to do in order to avoid being significantly compressed, or even buckled (note that the rod does indeed compress a little; we are implicitly ignoring this tiny deviation in its length and the resulting slight deviation from circular motion). ]
At the bottom of the arc the net force is toward the center and therefore upward.
- net force = rod force + weight
- rod force = net force - weight = 3.449 Newtons - (- 17.2382 Newtons) = 3.448 Newtons.
- The object needs a centripetal force in a direction opposed to its weight, so to keep it in the circular orbit the rod obliges by supplying an upward force in excess of the weight.
- [ Actually this is what the rod has to do in order to avoid being stretches out of shape or even pulled apart (note that the rod does indeed stretch a little; we are implicitly ignoring this tiny deviation in its length and the resulting slight deviation from circular motion). ]
At the height of the center the net force on the object is toward the center and therefore horizontal, perpendicular to the weight of the object.
An object of mass m moving on any circle with constant speed has acceleration aCent = v^2 / r. This is its only acceleration, since it is not changing velocity in the direction of its motion.
At any point of its arc is also experiences a downward gravitational force. If the upward direction is taken as positive we have
At any point the net force on the object is therefore the vector sum of its weight and the force exerted by whatever is holding it in its circular path--in this case the rod force:
At the top of the arc centripetal force is downward and we therefore have
At the bottom of the arc centripetal force is upward so that
At the altitude of the center of the circle we have
The figure below shows how at the top of a vertical circle the net force and gravitational forces are both downward, with the net force smaller than the gravitational force, while at the bottom the net force is upward and the gravitational force is downward.
In the 'middle' of the vertical circle the rod must supply the net force, which is in the horizontal direction, and counter the vertical gravitational force.
"